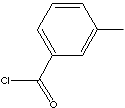
| m-TOLUOYL CHLORIDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 1711-06-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 216-976-8 | |
| FORMULA | CH3C6H4COCl | |
| MOL WT. | 154.60 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2916.39 | |
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3440mg/kg | |
| SYNONYMS | 3-Methylbenzoyl chloride; m-Toluyl chloride; | |
| 3-Methylbenzoic acid chloride; | ||
| SMILES | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | clear to pale yellow liquid | |
|
MELTING POINT |
||
| BOILING POINT | 220 C | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.173 | |
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Decomposes | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 3; Flammability: 2; Reactivity: 0 | |
| FLASH POINT |
82 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive. | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Acyl is a radical formed from an organic acid by removal of a hydroxyl group. The general formula of acyl compound is RCO-. Acyl halide is one of a large group of organic substances containing the halocarbonyl group, have the general formula RCO·X, where X is a halogen atom (fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine) and R may be aliphatic, alicyclic, aromatic, and H etc. In substitutive chemical nomenclature, their names are formed by adding '-oyl' as a suffix to the name of the parent compound; ethanoyl chloride, CH3COCl, is an example. The terms acyl and aroyl halides refer to aliphatic or aromatic derivatives, respectively. Acyl halides are made by replacing the -OH group in carboxylic acids by halogen using halogenating agents. They react readily with water, alcohols, and amines and are widely used in organic synthetic process whereby the acyl group is incorporated into the target molecules by substitution of addition-elimination sequence called acylation reaction. Acylation reaction involves substitution by an electron donor (nucleophile) at the electrophilic carbonyl group (C=O). Common nucleophiles in the acylation reaction are aliphatic and aromatic alcohols, both of which give rise to esters and amines (RNH2) which give amides. The carboxylic acid (X = OH) itself can function as an acylating agent when it is protonated by a strong acid catalyst as in the direct esterification of an alcohol. Two common acylation agents, with the general formula RCOX, are acid halides (X = halogen atom) and anhydrides (X = OCOR). Schotten-Baumann reaction is an acylation reaction that uses an acid chloride in the presence of dilute alkali to acylate the hydroxyl and amino group of organic compounds. There are also other acylating agents. Benzoyl Chloride belongs to acyl halides. Acyl halides are involved in acetylation process which introduce an acetyl group (CH3CO-) into compounds. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
clear to pale yellow liquid | |
| PURITY | 99.0% min | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 220kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | 8 (Packing Group: II) | |
| UN NO. | 1760 | |
| REMARKS | ||
| Hazard Symbols: C, Risk Phrases: 34-36/37, Safety Phrases: 23-26-36/37/39-45 | ||